Nanopore-only Microbial Isolate Sequencing Solution (NO-MISS) – automated ElysION (SQK-RBK114.96) (ISOE_9213_v114_revE_28Oct2025)
MinION: Protocol
Nanopore-only Microbial Isolate Sequencing Solution (NO-MISS) – automated ElysION (SQK-RBK114.96) V ISOE_9213_v114_revE_28Oct2025
This is an automated end-to-end method using the ElysION device outlining sample extraction, library preparation, sequencing, and analysis.
The protocol:
- Uses bacterial or fungi cells
- Enables multiplexing of up to 24 samples
- Includes DNA fragmentation
- Is optimised for high output
- Is compatible with R10.4.1 flow cells
For Research Use Only
This method is used with an Early Access device.
For more information about our Early Access programmes, please refer to this article on product release phases.
FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY
Contents
Introduction to the protocol
Sample sheet generation
Sample preparation
- 4. Option 1: Universal bead-beating sample preparation for ElysION
- 5. Option 2: Bacterial sample preparation for ElysION
- 6. Option 3: Hard to lyse organisms sample preparation for ElysION
Automated gDNA extraction, library preparation and sequencing
Troubleshooting
Appendix
Overview
This is an automated end-to-end method using the ElysION device outlining sample extraction, library preparation, sequencing, and analysis.
The protocol:
- Uses bacterial or fungi cells
- Enables multiplexing of up to 24 samples
- Includes DNA fragmentation
- Is optimised for high output
- Is compatible with R10.4.1 flow cells
For Research Use Only
This method is used with an Early Access device.
For more information about our Early Access programmes, please refer to this article on product release phases.
1. Overview of the protocol
This protocol is a work in progress and some details are expected to change over time. Please make sure you always use the most recent version of the protocol.
Introduction to the automated Nanopore-only Microbial Isolate Sequencing Solution (NO-MISS) protocol using ElysION
This end to end protocol describes our automated Nanopore-Only Microbial Isolate Sequencing Solution (NO-MISS): a flexible approach allowing sequencing of up to 24 microbial isolate genomes per MinION Flow Cell, generating a coverage of 50x per genome.
The 50x coverage threshold is sufficient for downstream analysis including: accurate assembly and plasmid resolution, AMR profiling, core genome (cg) and whole genome (wg) multi-locus sequence typing (MLST), and cg/wgSNP typing. Your sequencing data will be analysed by the device using the wf-bacterial-genomes workflow, which produces a user-friendly report of the results.
We provide multiple DNA extraction approaches, depending on requirements, and starting organism (bacteria, fungi/yeast). These are key in achieving reliable flow cell output and genome coverage.
The extracted gDNA is then tagmented and sequenced using our Rapid Barcoding Kit (SQK-RBK114.96). Up to 24 samples per sequencing experiment for bacterial isolates (up to 7 Mb genomes) and up to 8 samples for fungi/yeast isolates can be processed. Bacteria with a genome size of ≤4 Mb can be expected to generate a minimum coverage of 50x per genome. Please note, coverage may vary depending on larger genome size and input sample quality.
We recommend sequencing up to 72 hours and generating at least 50x coverage per sample (approx. 0.5 Gb per barcode, assuming 5 Mb genome).
Steps in the sequencing workflow:
Prepare for your experiment
You will need to:
- Ensure your ElysION device is installed with the required hardware and software package for this workflow.
- Ensure you have your sequencing kit, the correct equipment and third-party reagents.
- Check your flow cell to ensure it has enough pores for a good sequencing run.
Sample preparation
We have developed several optimised extraction methods to generate high quality genomic DNA from your cell cultures, allowing maximised sequencing output using the automated Nanopore-only Microbial Isolate Sequencing Solution (NO-MISS) end-to-end protocol.
What extraction method is right for me?

Using the relevant gDNA extraction method, you will need to lyse your cells and extract your gDNA:
Universal bead-beating method:
- For high throughput requirements and universal applications, including bacteria and fungi.
Bacteria gDNA extraction:
- This extraction method is recommended for use with general bacterial samples. This method has been validated with Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Serratia marcescens, Enterococcus faecalis, and Bacillus subtilis or staphylococci such as Staphylococcus aureus, and Staphylococcus epidermidis.
Hard to lyse organisms for gDNA extraction:
- This extraction method is recommended for hard to lyse organisms, such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, or for bacteria that was not successfully extracted using the Bacterial gDNA extraction method.
Automated library preparation, sequencing and analysis

The Table below is an overview of the steps automated by the ElysION device.
| Library preparation step | Process |
|---|---|
| Sample extraction | |
| Bead binding | Addition of the DNA binding bead mix from the MagMAX™ DNA Multi-Sample Ultra 2.0 Kit to your lysed sample(s) |
| Clean-up | gDNA purification and clean-up |
| Elution | Elution of your extracted and cleaned sample gDNA |
| Library preparation | |
| DNA barcoding | Tagmentation of the DNA using the Rapid Barcoding Kit V14 |
| Sample pooling | Pooling of barcoded samples |
| Bead binding | Addition of AMPure XP Beads |
| Flow cell priming | Prime the flow cell for sequencing |
| Clean-up | Clean-up your samples by performing an ethanol wash. |
| Elution | Elute the pooled and cleaned DNA, and attach the sequencing adapters to the DNA ends. |
| Flow cell loading | Prime the flow cell and load the prepared library for sequencing. |
| Sequencing | Your sequencing run uses the Gourami software, which will collect raw data to basecall and demultiplex the barcoded reads. |
| Data analysis | Once sequencing is complete, the device will perform downstream analysis of the data using the isolate mode of the wf-bacterial-genomes workflow. |
| Flow cell wash or flush | Flow cell is washed using the EXP-WSH004 for reuse or flushed for return. |
Compatibility of this protocol
This protocol should only be used in combination with:
- Rapid Barcoding Kit 96 V14 (SQK-RBK114.96)
- R10.4.1 flow cells (FLO-MIN114)
- Flow Cell Wash Kit (EXP-WSH004)
- Flow Cell Priming Kit V14 (EXP-FLP004)
- Sequencing Auxiliary Vials V14 (EXP-AUX003)
- Rapid Adapter Auxiliary V14 (EXP-RAA114)
- ElysION device
2. Equipment and consumables
Materials
- Sample input for DNA extraction (see details below)
- Rapid Barcoding Kit 96 V14 (SQK-RBK114.96)
- Flow Cell Wash Kit (EXP-WSH004)
Consumables
- MinION/GridION Flow Cell
- MagMAX™ DNA Multi-Sample Ultra 2.0 Kit (ThermoFisher, A36570)
- MagMAX™ DNA Cell and Tissue Extraction Buffer (ThermoFisher, A45469)
- PureLink™ RNase A (20 mg/ml) (ThermoFisher, 12091021)
- PBS pH 7.4 (e.g. Gibco, 11503387)
- TE Buffer Solution pH 8.0 (Sigma, 8890-OP)
- Lysozyme human (Sigma, L1667)
- Achromopeptidase (Sigma, A3547)
- 5 M Sodium chloride NaCl (Sigma, 71386)
- Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate SDS (Sigma, 71736)
- Trizma® hydrochloride solution (Sigma, T2819)
- BashingBead Buffer (Zymo, D6001-3-40)
- Empty FastPrep® 2 ml Lysing Matrix tubes (MP Biomedicals, 115076200)
- Screw Cap for 2 ml Lysing Matrix tubes (MP Biomedicals, 115067005)
- Glass beads, 4 mm (MP Biomedicals, 116914801)
- PowerBead Pro tube (Qiagen, 19301)
- Hard-Shell® 96-Well PCR Plates, low profile, thin wall, skirted, red/clear (Bio-Rad™, HSP9611)
- Nunc™ 96 Well Polypropylene 2 ml DeepWell Plate (ThermoFisher, 95040452)
- ElysION Disposable Tips - 1000 µl (ELY-TIP1000)
- ElysION Disposable Tips - 200 µl (ELY-TIP0200)
- ElysION Disposable Tips - 50 µl (ELY-TIP0050)
- ElysION Disposable Tips Box Small (ELY-TBS01)
- ElysION Disposable Tips Box Large (ELY-TBL01)
- Reservoir Plate (Porvair, 390015)
- Azenta PCR Plate Lid (Azenta, 4ti-0291)
- Screw Cap Micro tube 2 ml, sterile (Sarstedt™, 72.694.006)
- Screw Cap Micro tube 0.5 ml, sterile (Sarstedt™, 72.730.106)
- ElysION Waste Bin (ELY-WB01)
- 10 µl inoculating loop
- Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) (50 mg/ml) (e.g Invitrogen™ UltraPure™ BSA 50 mg/ml, AM2616)
- Freshly prepared 80% ethanol in nuclease-free water
- Nuclease-free water (e.g. Thermo Scientific, AM9937)
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes
- 0.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes
Equipment
- ElysION device with MinION integration
- MinION/GridION Flow Cell Light Shield
- Vortex mixer (Vortex-Genie 2, Scientific Industries SI™ SI-0266)
- Vortex Adapter (Qiagen, 13000-V1-24)
- Thermal cycler
- Timer
- Thermomixer e.g. Eppendorf F2.0 Model (Fisher, 15356551)
- Magnetic separation rack
- Microplate centrifuge
- Centrifuge e.g. Eppendorf max speed 15,000rpm (Fisher, 15881635)
- Multichannel pipette and tips
- P1000 pipette and tips
- P200 pipette and tips
- P100 pipette and tips
- P20 pipette and tips
- P2 pipette and tips
- Ice bucket with ice
Optional equipment
- Hula mixer (gentle rotator mixer)
- Qubit™ fluorometer (or equivalent for QC check)
The above list of materials, consumables, and equipment is for all the extraction methods in the sample preparation section, as well as the library preparation section of the protocol. You will only need the consumables for the relevant extraction method for your sample input and the library preparation section.
For this protocol, the following inputs are required per sample:
| Sample extraction method | Sample type | Sample input | Expected yield | Expected DNA Integrity Number (DIN) | Average sequencing read lengths |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Universal bead-beating gDNA extraction | Universal applications: bacteria, fungi or yeast | 1 ml liquid overnight culture (~1 x 10^8 – 10^9 cfu/ml) or half of a loop of colonies from a plate | >200 ng/µl per sample | 7-9 | ~4-7 kb |
| Bacteria gDNA extraction | Bacterial | 200 µl liquid overnight culture (~1 x 10^8 – 10^9 cfu/ml) or 1/8 of a loop of colonies from a plate | 15-20 ng/µl per sample | 9 | >7 kb - Size will vary based on sample input species |
| Hard to lyse organisms gDNA extraction | Hard to extract bacterial samples (e.g. Mycobacterium tuberculosis) | For hard to lyse bacterial samples: 200 µl liquid overnight culture (~1 x 10^8 – 10^9 cfu/ml) or 1/8 of a loop of colonies from a plate For Mycobacterium tuberculosis: 5 – 10 mg cells from solid or liquid media | 15-40 ng/µl per sample | 8 | >7 kb - Size will vary based on sample input species |
Note: The output and, sequencing read length of extracted DNA may vary depending on sample quality and species. Please ensure you are following the correct method and using high-quality sample inputs.
For staphylococcal inputs
Staphylococcal Lysis Buffer (SLB) is required for the bacterial gDNA extraction method for staphylococcal inputs.
| Reagent | Stock | Final concentration | Volume for 12 samples with excess | Volume for 24 samples with excess |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trizma hydrochloride solution, pH 9 | 1 M | 100 mM | 150 µl | 300 µl |
| Sodium chloride | 5 M | 10 mM | 3 µl | 6 µl |
| SDS | 10% v/v | 0.1% v/v | 15 µl | 30 µl |
| Nuclease-free water | - | - | 1,332 µl | 2,664 µl |
| Total volume | - | - | 1,500 µl | 3,000 µl |
The SDS in the Staphylococcal Lysis Buffer (SLB) is essential for preventing the degradation of staphylococci DNA. Exclusion of SDS from the buffer results in a larger smear of DNA when run on a gel.
Third-party reagents
Depending on the extraction protocol used, not all third-party reagents are required.
We have validated and recommend the use of all the third-party reagents used in this protocol. Alternatives have not been tested by Oxford Nanopore Technologies.
For all third-party reagents, we recommend following the manufacturer's instructions to prepare the reagents for use.
Check your flow cell
The number of pores in your flow cell will be checked by the ElysION device at the start of your assay. Flow cells should be checked within 12 weeks of purchasing your MinION/GridION Flow Cells.
Oxford Nanopore Technologies will replace any unused flow cell with fewer than the number of pores listed in the Table below, when the result is reported within two days of performing the flow cell check, and when the storage recommendations have been followed. To do the flow cell check, please follow the instructions on the ElysION on-screen display.
| Flow cell | Minimum number of active pores covered by warranty |
|---|---|
| MinION/GridION Flow Cell | 800 |
The Rapid Adapter (RA) used in this kit and protocol is not interchangeable with other sequencing adapters.
Rapid Barcoding Kit 96 V14 (SQK-RBK114.96) contents
| Name | Acronym | Cap colour | No. of vials | Fill volume per vial (µl) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rapid Adapter | RA | Green | 2 | 15 |
| Adapter Buffer | ADB | Clear | 1 | 100 |
| AMPure XP Beads | AXP | Amber | 3 | 1,200 |
| Elution Buffer | EB | Black | 1 | 1,500 |
| Sequencing Buffer | SB | Red | 1 | 1,700 |
| Library Beads | LIB | Pink | 1 | 1,800 |
| Library Solution | LIS | White cap, pink label | 1 | 1,800 |
| Flow Cell Flush | FCF | Clear | 1 | 15,500 |
| Flow Cell Tether | FCT | Purple | 2 | 200 |
| Rapid Barcodes | RB01-96 | - | 3 plates | 8 µl per well |
This product contains AMPure XP reagent manufactured by Beckman Coulter, Inc. and can be stored at -20°C with the kit without detriment to reagent stability.
3. ElysION NO-MISS sample sheet setup
Sample sheet information
The sample sheet assigns a barcode to each sample, allowing a user to pick a range from the 96-well plate, and for a sample ID to be tracked from input to results.
For more information on setting up a sample sheet please refer to the ElysION User Guide.
Set up your sample sheet as a CSV file with the following information:
| Required field | User input | Definition / field info |
|---|---|---|
| v1 | Version field, no input required outside of field | |
| assay | isoseq-1-24:v1.1 | Assay ID and version |
| library_id | User-defined | Identification for the DNA library |
| created_by | User-defined | Identification of operator setting up sample sheet |
| created_at | User-defined | Date and time of creation. Please follow the format outlined in the ElysION user guide |
| sample_count | User-defined | Number of samples processed in run (up to 24 samples) |
| well_id | A1-H3 | Positions in 96-well plate being used (up to 24 samples). Samples must start from position A1 in the 96-well plate and run consecutively column-wise. |
| barcode | barcode01-barcode96 | Rapid barcodes from SQK-RBK114.96 being used in library preparation. Up to 96 barcodes are available in the sequencing kit, these should be used in sub-sets of up to 24 barcodes, used sequentially. (e.g. Barcodes 01-24, or Barcodes 50-60) |
| sample_type | User-defined | Description or characteristics of sample input |
| sample_id | User-defined from LIMS system (lims-sampleid-12345) | Identification for each sample input (e.g. from LIMS system) |
Below is an example of a sample sheet CSV file for 10 samples:

4. Option 1: Universal bead-beating sample preparation for ElysION
Materials
- 1 ml liquid overnight culture (~1 x 10^8 – 10^9 cfu/ml) OR half of a loop of colonies from a plate
Consumables
- Proteinase K (from the MagMAX DNA Multi-Sample Ultra 2.0 Kit)
- PureLink™ RNase A (20 mg/ml) (ThermoFisher, 12091021)
- PBS pH 7.4 (e.g. Gibco, 11503387)
- BashingBead Buffer (Zymo, D6001-3-40)
- PowerBead Pro tube (Qiagen, 19301)
- Nuclease-free water (e.g. Thermo Scientific, AM9937)
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes
- Nunc™ 96 Well Polypropylene 2 ml DeepWell Plate (ThermoFisher, 95040452)
- 10 µl inoculating loop
Equipment
- Vortex Adapter (Qiagen, 13000-V1-24)
- Eppendorf 5424 centrifuge (or equivalent)
- Thermomixer
- Vortex mixer
- P1000 pipette and tips
- P200 pipette and tips
- P20 pipette and tips
- P2 pipette and tips
Optional equipment
- Hula mixer (gentle rotator mixer)
Universal bead-beating gDNA extraction
This extraction method is a universal gDNA extraction from bacteria and fungi/yeast. It uses vortex bead-beating followed by a proteinase K and RNase treatment.
Note: If your desired yield is not achieved or you are looking to maximise the contiguity of your assemblies by generating longer read lengths, try one of our sample-tailored extraction methods:
- Bacteria gDNA extraction
- Hard to lyse organisms gDNA extraction
Extraction method overview: Universal bead-beating gDNA extraction for ElysION
| Sample extraction method | Sample type | Sample input | Expected yield | Expected DNA Integrity Number (DIN) | Average sequencing read lengths |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Universal bead-beating gDNA extraction | Universal applications: bacteria, fungi or yeast | 1 ml liquid overnight culture (~1 x 10^8 – 10^9 cfu/ml) or half of a loop of colonies from a plate | >200 ng/µl per sample | 7-9 | ~4-7 kb |
Note: The output, and sequencing read length of extracted DNA may vary depending on sample quality and species. Please ensure you are following the correct method and using high-quality sample inputs.
Prepare your sample depending on your sample type by following the instructions below:
| If using liquid media for your culture: |
|---|
| 1. Centrifuge 1 ml liquid overnight culture (~10^8 – 10^9 cfu/ml) at 12,000 x g for 1 minute. |
| 2. Remove the supernatant and resuspend the pellet in 1 ml Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS). Note: Washing the sample by removing the supernatant and resuspending the pellet in clean Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS) removes potential inhibitors from the nutrient broth and removes free DNA that may be degraded. |
| 3. Centrifuge at 12,000 x g 1 minute. |
| 4. Remove the supernatant, without disturbing the pellet. |
| 5. Resuspend the pellet in 350 µl bashing bead buffer (Zymo, D6001-3-40). |
| 6. Add the 350 µl of resuspended sample to a PowerBead Pro tube (Qiagen, 19301). |
| 7. Take forward the PowerBead Pro tube containing 350 µl of resuspended sample into the next step. |
| If using solid media for your culture: |
|---|
| 1. Add 350 µl BashingBead Buffer (Zymo, D6001-3-40) to a PowerBead Pro tube (Qiagen, 19301). |
| 2. Using a sterile 10 µl inoculating loop, pick half a loop worth of colonies, avoiding scratching the agar. |
| 3. Place the inoculating loop with the colonies in the PowerBead Pro tube containing the BashingBead Buffer, and agitate to relieve the cells into the tube. |
| 4. Discard the used inoculating loop. |
| 5. Take forward the PowerBead Pro tube containing 350 µl of resuspended sample into the next step. |
Secure the PowerBead tube(s) containing your 350 µl of resuspended sample from the previous step to a vortex mixer using a Vortex Adapter (e.g. Qiagen, 13000-V1-24).
Vortex at maximum speed for 10 minutes (~3,000 RPM).
Centrifuge the tube(s) containing your sample at 12,000 x g for 30 seconds.
Transfer the supernatant from the bead-beating tube into a clean 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube.
Note: Expect ~200–250 µl of supernatant.
Add the following reagents with your sample in the 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube, and mix by vortexing.
For bacterial samples:
| Reagent | Volume |
|---|---|
| Proteinase K | 10 µl |
| RNase A | 3 µl |
For fungi/yeast samples:
| Reagent | Volume |
|---|---|
| Proteinase K | 30 µl |
| RNase A | 3 µl |
The full 15-minute incubation must be completed to ensure the proteinase and RNase activity occurs, regardless of turbidity.
Incubate at 56°C for 15 minutes in a thermomixer at 1,000 RPM.
Note: Depending on the bacterial input, the solution may become fully transparent or may remain hazy.
Spin down the sample tube(s) and transfer the full sample volume into a Nunc™ 96 Well 2 ml DeepWell Plate for library preparation on the ElysION.
Note: Ensure you keep your samples separate, with each sample being transferred into a separate well of the Nunc™ 96 Well 2 ml DeepWell Plate.
Take forward the Nunc™ 96 Well 2 ml DeepWell Plate containing your sample(s) into the automated gDNA extraction and library preparation section of this protocol.
5. Option 2: Bacterial sample preparation for ElysION
Materials
- 200 µl liquid overnight culture (~1 x 10^8 – 10^9 cfu/ml) OR 1/8 of a loop of colonies from a plate
Consumables
- PBS pH 7.4 (e.g. Gibco, 11503387)
- TE Buffer Solution pH 8.0 (Sigma, 8890-OP)
- Lysozyme human (Sigma, L1667)
- Staphylococcal Lysis Buffer (SLB) (100 mM Tris pH9, 10 mM NaCl, 0.1% SDS)
- 10 µl inoculating loop
- Proteinase K (from the MagMAX DNA Multi-Sample Ultra 2.0 Kit)
- PureLink™ RNase A (20 mg/ml) (ThermoFisher, 12091021)
- MagMAX™ DNA Cell and Tissue Extraction Buffer (ThermoFisher, A45469)
- Nuclease-free water (e.g. Thermo Scientific, AM9937)
- Achromopeptidase (Sigma, A3547)
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes
- 5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes
- Nunc™ 96 Well Polypropylene 2 ml DeepWell Plate (ThermoFisher, 95040452)
Equipment
- Eppendorf 5424 centrifuge (or equivalent)
- Thermomixer
- Vortex mixer
- P1000 pipette and tips
- P200 pipette and tips
- P100 pipette and tips
- P20 pipette and tips
- P2 pipette and tips
Bacteria gDNA extraction
This extraction protocol is recommended for use with general bacterial samples. We have validated this method with Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Serratia marcescens, Enterococcus faecalis, and Bacillus subtilis or staphylococci such as Staphylococcus aureus, and Staphylococcus epidermidis.
If the desired yield is not achieved from your extraction, try one of the following recommendations:
- The enzymatic reaction time in step 7 can be increased.
- Use the staphylococcal enzyme.
- Follow the Hard to lyse organisms gDNA extraction method.
Extraction method overview: Bacteria gDNA extraction for ElysION
| Sample extraction method | Sample type | Sample input | Expected yield | Expected DNA Integrity Number (DIN) | Average sequencing read lengths |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria gDNA extraction | Bacterial | 200 µl liquid overnight culture (~1 x 10^8 – 10^9 cfu/ml) or 1/8 of a loop of colonies from a plate | 15-20 ng/µl per sample | 9 | >7 kb - Size will vary based on sample input species |
Note: The output, and sequencing read length of extracted DNA may vary depending on sample quality and species. Please ensure you are following the correct method and using high-quality sample inputs.
Reconstitute your sample depending on your sample type by following the instructions below:
| For general bacterial inputs: |
|---|
| 1. Reconstitute the bacterial lysozyme in TE buffer to 10 mg/ml. Note: The lysozyme can be stored at 100 mg/ml in a stabilised solution for long-term use as follows: 25 mM Sodium acetate, 50% glycerol, 100 mg/ml lysozyme – stored at -20°C. |
| For staphylococcal inputs: |
|---|
| 1. Prepare the Staphylococcal Lysis Buffer (SLB) (100 mM Tris pH9, 10 mM NaCl, 0.1% SDS). Information for preparing the Staphylococcal Lysis Buffer (SLB) can be found in the Equipment and consumables section of this protocol. |
| 2. Reconstitute the achromopeptidase in nuclease-free water to 10 mg/ml. |
Tip: We recommend preparing enzymes freshly on the day as enzymatic activity reduces over time once reconstituted.
Prepare your sample depending on your sample type by following the instructions below:
| If using liquid media for your culture: |
|---|
| 1. Centrifuge 200 µl liquid overnight culture (~10^8 – 10^9 cfu/ml) at 12,000 x g for 1 minute. |
| 2. Remove the supernatant and resuspend the pellet in 1 ml Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS). Note: Washing the sample by removing the supernatant and resuspending the pellet in clean Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS) removes potential inhibitors from the nutrient broth and removes free DNA that may be degraded. |
| 3. Centrifuge at 12,000 x g 1 minute. |
| 4. Remove the supernatant, without disturbing the pellet. Note: It is important to remove as much PBS as possible without disturbing the pellet as the buffer has an inhibitory effect on enzyme activity. |
| 5. Resuspend the pellet depending on your input type: For bacterial samples: resuspend the pellet in 100 µl TE buffer with 10 µl lysozyme (10 mg/ml). For staphylococci samples: Resuspend the pellet in 100 µl SLB with 10 µl achromopeptidase (10 mg/ml). |
| If using solid media for your culture: |
|---|
| 1. Add 1 ml of PBS to a fresh 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube. |
| 2. Using a sterile 10 µl inoculating loop, pick 1/8 a loop worth of colonies, avoiding scratching the agar. |
| 3. Place the inoculating loop with the colonies in the tube containing the PBS, and agitate to relieve the cells into the tube. |
| 4. Discard the used inoculating loop. |
| 5. Centrifuge at 12,000 x g 1 minute. |
| 6. Remove the supernatant, without disturbing the pellet. Note: It is important to remove as much PBS as possible without disturbing the pellet as the buffer has an inhibitory effect on enzyme activity. |
| 7. Resuspend the pellet depending on your input type: For bacterial samples: resuspend the pellet in 100 µl TE buffer with 10 µl lysozyme (10 mg/ml). For staphylococci samples: Resuspend the pellet in 100 µl SLB with 10 µl achromopeptidase (10 mg/ml). |
Incubate at 37°C for 10 minutes in a thermomixer at 500 RPM.
If a thermomixer is unavailable, the reaction can be incubated stationary and agitated by gently flicking for 10 seconds every two minutes.
Combine the following reagents with your sample in the 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube, and mix by pipetting.
| Reagent | Volume |
|---|---|
| Proteinase K | 10 µl |
| RNase A | 3 µl |
| Total (including your sample) | 113 µl |
Add 500 µl MagMAX™ DNA Cell and Tissue Extraction Buffer, mix and spin down.
The full 30-minute incubation must be completed to ensure the proteinase and RNase activity occurs, regardless of turbidity.
Incubate at 56°C for 30 minutes in a thermomixer at 1,000 RPM.
Note: Depending on the bacterial input, the solution may become fully transparent or may remain hazy.
Spin down the sample tube(s) and transfer the full sample volume into a Nunc™ 96 Well 2 ml DeepWell Plate for library preparation on the ElysION.
Note: Ensure you keep your samples separate, with each sample being transferred into a separate well of the Nunc™ 96 Well 2 ml DeepWell Plate.
Take forward the Nunc™ 96 Well 2 ml DeepWell Plate containing your sample(s) into the automated gDNA extraction and library preparation section of this protocol.
6. Option 3: Hard to lyse organisms sample preparation for ElysION
Materials
- For hard to lyse bacterial samples: 200 µl liquid overnight culture (~1 x 10^8 – 10^9 cfu/ml) OR 1/8 of a loop of colonies from a plate
- For Mycobacterium tuberculosis: 5 – 10 mg cells from solid or liquid media
Consumables
- PBS pH 7.4 (e.g. Gibco, 11503387)
- TE Buffer Solution pH 8.0 (Sigma, 8890-OP)
- Lysozyme human (Sigma, L1667)
- Glass beads, 4 mm (MP Biomedicals, 116914801)
- 10 µl inoculating loop
- Proteinase K (from the MagMAX DNA Multi-Sample Ultra 2.0 Kit)
- PureLink™ RNase A (20 mg/ml) (ThermoFisher, 12091021)
- MagMAX™ DNA Cell and Tissue Extraction Buffer (ThermoFisher, A45469)
- 5 M Sodium chloride NaCl (Sigma, 71386)
- Nuclease-free water (e.g. Thermo Scientific, AM9937)
- Empty FastPrep® 2 ml Lysing Matrix tubes (MP Biomedicals, 115076200)
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes
- Nunc™ 96 Well Polypropylene 2 ml DeepWell Plate (ThermoFisher, 95040452)
Equipment
- Eppendorf 5424 centrifuge (or equivalent)
- Thermomixer
- Vortex mixer
- P1000 pipette and tips
- P200 pipette and tips
- P100 pipette and tips
- P20 pipette and tips
- P2 pipette and tips
Hard to lyse organisms gDNA extraction
This extraction method is recommended for hard to lyse organisms, such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, or for bacteria that was not successfully extracted using the Bacteria gDNA extraction method.
Extraction method overview: Hard to lyse organisms gDNA extraction for ElysION
| Sample extraction method | Sample type | Sample input | Expected yield | Expected DNA Integrity Number (DIN) | Average sequencing read lengths |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hard to lyse organisms gDNA extraction | Hard to extract bacterial samples (e.g. Mycobacterium tuberculosis) | For hard to lyse bacterial samples: 200 µl liquid overnight culture (~1 x 10^8 – 10^9 cfu/ml) or 1/8 of a loop of colonies from a plate For Mycobacterium tuberculosis: 5 – 10 mg cells from solid or liquid media | 15-40 ng/µl per sample | 8 | >7 kb - Size will vary based on sample input species |
Note: The output, and sequencing read length of extracted DNA may vary depending on sample quality and species. Please ensure you are following the correct method and using high-quality sample inputs.
We recommend preparing enzymes freshly on the day as enzymatic activity reduces over time, once reconstituted.
Prepare the lysozyme by reconstituting in TE buffer to 10 mg/ml.
Prepare your sample depending on your sample type by following the instructions below:
For hard to lyse bacterial samples
| If using liquid media for your culture: |
|---|
| 1. Centrifuge 200 µl liquid overnight culture (~10^8 – 10^9 cfu/ml) at 12,000 x g for 1 minute. |
| 2. Remove the supernatant without disturbing the pellet. |
| If using solid media for your culture: |
|---|
| 1. Using a sterile 10 µl inoculating loop, collect 1/8 a loop worth of colonies into a fresh 1.5 ml Eppendorf tube, avoiding scratching the agar. |
For Mycobacterium tuberculosis samples
IMPORTANT: For Mycobacterium tuberculosis, we recommend avoiding overgrowing the cultures:
- For Mycobacterium tuberculosis solid media: ~2-4 weeks of growth should provide sufficient biomass.
- For Mycobacterium tuberculosis liquid media: ~ 2 weeks of growth should provide sufficient biomass.
We also strongly advise harvesting the recommended amount of input material to yield the correct amount of gDNA for the library preparation step.
Less than 5 mg will not yield enough gDNA for library preparation (less than 10 ng/µl), negatively impacting sequencing output.
More than 10 mg may result in carryover of sequencing inhibitors onto the flow cell, also negatively impacting sequencing output.
| For Mycobacterium tuberculosis solid media: |
|---|
| 1. Harvest 5-10 mg of cells from your Mycobacterium tuberculosis solid media and transfer to a 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube. |
| For Mycobacterium tuberculosis liquid media: |
|---|
| 1. Add ~500 µl of Mycobacterium tuberculosis liquid media to a fresh 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube. |
| 2. Centrifuge at 12,000 x g 1 minute. |
| 3. Remove the supernatant, without disturbing the pellet. |
| 4. Harvest 5-10 mg of cells from the pellet and transfer to a 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube. |
Resuspend the pellet in 500 µl PBS and pipette mix using a P1000 pipette.
If the pipette tip becomes clogged, gently press the pipette tip down on the bottom of the tube to break up clumps while pipetting up and down.
Incubate the sample at 80°C for 20 minutes.
We do not recommend increasing the temperature of the incubation as this may negatively impact DNA quality and sequencing data.
This heated incubation is important for efficient cell lysis.
Centrifuge at 12,000 x g for 1 minute.
Remove the supernatant without disturbing the pellet, then resuspend the pellet in 500 µl of fresh PBS.
Centrifuge at 12,000 x g for 1 minute.
Remove the supernatant and resuspend in 100 µl of TE buffer (10 mM Tris, pH 8 and 1 mM EDTA).
Transfer 100 µl of your sample to an empty 2 ml FastPrep lysing matrix tube and add two, 4 mm glass beads.
Vortex the sample for 30 seconds.
Vortexing with beads helps homogenise the sample to improve efficiency of later steps. Using 4 mm beads avoids overshearing of the DNA.
Add 10 µl lysozyme and mix by pulse vortexing.
Light agitation prevents aggregation and precipitation in the reaction and allows the enzyme to access the cell walls.
Incubate at 37°C for 15 minutes at 800 RPM in a thermomixer.
Constant shaking is essential to achieve sufficient lysis within 15 minutes and occasional agitation may not prevent the cells from clumping.
Note: If a thermomixer is not available, briefly vortex at regular intervals of 2 minutes.
Combine the following reagents with your sample in the 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube, and mix by pipetting.
| Reagent | Volume |
|---|---|
| Proteinase K | 10 µl |
| RNase A | 3 µl |
| Total (including your sample) | 123 µl |
Add 500 µl MagMAX™ DNA Cell and Tissue Extraction Buffer, mix and spin down.
Incubate at 56°C for 30 minutes in a thermomixer at 1,000 RPM.
Note: Depending on the bacterial input, the solution may become fully transparent or may remain hazy.
The full 30-minute incubation must be completed to ensure the proteinase and RNase activity occurs, regardless of turbidity.
Add 100 µl 5 M sodium chloride and centrifuge at 17,000 x g for 5 minutes.
The high salt step reduces yield but is essential to remove any inhibitors of the library preparation.
Avoiding the pellet, transfer 623 µl of the sample supernatant into a Nunc™ 96 Well 2 ml DeepWell Plate for library preparation on the ElysION.
Note: Ensure you keep your samples separate, with each sample being transferred into a separate well of the Nunc™ 96 Well 2 ml DeepWell Plate.
Take forward the Nunc™ 96 Well 2 ml DeepWell Plate containing your sample(s) into the automated gDNA extraction and library preparation section of this protocol.
7. ElysION run setup
Materials
- Rapid Barcoding Kit 96 V14 (SQK-RBK114.96)
- Flow Cell Wash Kit (EXP-WSH004)
Consumables
- MagMAX™ DNA Multi-Sample Ultra 2.0 Kit (ThermoFisher, A36570)
- Hard-Shell® 96-Well PCR Plates, low profile, thin wall, skirted, red/clear (Bio-Rad™, HSP9611)
- Nunc™ 96 Well Polypropylene 2 ml DeepWell Plate (ThermoFisher, 95040452)
- ElysION Disposable Tips - 1000 µl (ELY-TIP1000)
- ElysION Disposable Tips - 200 µl (ELY-TIP0200)
- ElysION Disposable Tips - 50 µl (ELY-TIP0050)
- ElysION Disposable Tips Box Small (ELY-TBS01)
- ElysION Disposable Tips Box Large (ELY-TBL01)
- Reservoir Plate (Porvair, 390015)
- Azenta PCR Plate Lid (Azenta, 4ti-0291)
- Screw Cap Micro tube 2 ml, sterile (Sarstedt™, 72.694.006)
- Screw Cap Micro tube 0.5 ml, sterile (Sarstedt™, 72.730.106)
- ElysION Waste Bin (ELY-WB01)
- Freshly prepared 80% ethanol in nuclease-free water
- Nuclease-free water (e.g. Thermo Scientific, AM9937)
- Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) (50 mg/ml) (e.g Invitrogen™ UltraPure™ BSA 50 mg/ml, AM2616)
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes
- 0.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes
Equipment
- Microfuge
- Vortex mixer (Vortex-Genie 2, Scientific Industries SI™ SI-0266)
- Microplate centrifuge
- P1000 pipette and tips
- P200 pipette and tips
- P100 pipette and tips
- P20 pipette and tips
- P10 pipette and tips
- P2 pipette and tips
- Multichannel pipette and tips
- Ice bucket with ice
The automated sample extraction, library preparation and sequencing method using the ElysION device can be followed using the on-screen display on the device.
Please ensure you have all the correct hardware components, software packages and workflows installed to carry out this method.
For more information on the device and the processes please refer to the ElysION User Guide.
It is possible to add a scheduled pause to allow for sample QC checks following automated DNA extraction on the ElysION.
To include a Pause for QC step in your ElysION run setup, please refer to the instructions in the Appendix of this protocol.
Thaw kit components at room temperature, spin down briefly using a microfuge and mix by pipetting as indicated by the Table below:
| Reagent | 1. Thaw at room temperature | 2. Briefly spin down | 3. Mix well by pipetting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rapid Barcode Plate (RB01-96) | Not frozen | ✓ | ✓ |
| Rapid Adapter (RA) | Not frozen | ✓ | ✓ |
| AMPure XP Beads (AXP) | ✓ | ✓ | Mix by pipetting or vortexing immediately before use |
| Elution Buffer (EB) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Adapter Buffer (ADB) | ✓ | ✓ | Mix by vortexing |
| Flow Cell Flush (FCF) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Flow Cell Tether (FCT) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Sequencing Buffer (SB) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Library Beads (LIB) | ✓ | ✓ | Mix by pipetting or vortexing immediately before use |
| Wash Mix (WMX) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Wash Diluent (DIL) | ✓ | ✓ | Mix by vortexing |
| Storage Buffer (S) | ✓ | ✓ | Mix by vortexing |
| Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
The wells of the barcoding plate are intended for single use only. Please ensure your barcode well is sealed before use, and do not reuse the barcode well once pierced/opened.
Thoroughly mix and resuspend the Binding Beads from the MagMAX DNA Multi-Sample Ultra 2.0 Kit by vortexing.
Prepare the DNA Binding Bead Mix as instructed below:
Note: The volumes will change depending on the number of samples being processed.
For runs with 1-9 samples
Use the Sarstedt Screw Cap Micro tube 2 ml, with 1,980 µl DNA Binding Bead Mix in each tube per 3 samples.
| Reagent | Volume for 1-3 samples (1x Sarstedt tube) | For 4-6 samples (2x Sarstedt tubes) | For 7-9 samples (3x Sarstedt tubes) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lysis/Binding Solution | 1.8 ml | 3.6 ml | 5.4 ml |
| Binding Beads | 180 µl | 360 µl | 540 µl |
| Total volume | 1,980 µl | 3,960 µl | 5,940 µl |
For runs with 10-24 samples
Use the reservoir plate, with 6 ml of DNA Binding Bead Mix + 600 µl additional volume per sample being processed.
| Reagent | For 10 samples (Reservoir Plate) | For 12 samples (Reservoir Plate) | For 18 samples (Reservoir Plate) | For 24 samples (Reservoir Plate) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lysis/Binding Solution | 5,455 µl + 5,455 µl = 10,910 µl | 5,455 µl + 6,545 µl = 12,000 µl | 5,455 µl + 9,818 µl = 15,273 µl | 5,455 µl + 13,090 µl = 18,545 µl |
| Binding Beads | 545 µl + 545 µl = 1,090 µl | 545 µl + 655 µl = 1,200 µl | 545 µl + 982 µl = 1,527 µl | 545 µl + 1,310 µl = 1,855 µl |
| Total volume | 6,000 µl + 6,000 µl = 12,000 µl | 6,000 µl + 7,200 µl = 13,200 µl | 6,000 µl + 10,800 µl = 16,800 µl | 6,000 µl + 14,400 µl = 20,400 µl |
Switch on the ElysION device and its computer following the user guide.
The Background Services application must run continuously whilst using the ElysION, and should not be closed.
Ensure the Background Services application is running.
If the application is not running, double click the Background Services desktop application on your ElysION device.
Open the ElysION UI application.
Ensure the ElysION deck is clear of any labware before performing automated checks.
Failure to ensure the deck is clear can lead to errors in checks or damage to the equipment.
Close the door to the robot and select "Initialise" on the display.
Note: The ElysION device will perform automated checks.
Allow the initialisation checks to complete before proceeding with the library preparation method.
It is possible to add a scheduled pause to allow for sample QC checks following automated DNA extraction on the ElysION.
To include a Pause for QC step in your ElysION run setup, please refer to the instructions in the Appendix of this protocol.
Select "Run method" on the on-screen display.
Select the method “Nanopore-only Microbial Isolate Sequencing Solution” on the on-screen display.
Click Next to proceed.
Insert a MinION and GridION Flow Cell into the MinION Mk1D device on the ElysION deck.
Instructions for inserting a flow cell onto the ElysION device can be found in the ElysION User Guide.
Select "Check flow cell" on the on-screen display.
Once flow cell check begins, click Next to proceed.
Select "Import" on the on-screen display to upload your sample sheet.
Once completed click Next to proceed.
In a new 0.5 ml Sarstedt Screw tube, prepare the Rapid Adapter Master Mix as follows and pipette mix:
| Reagent | Volume |
|---|---|
| Rapid Adapter (RA) | 1.5 μl |
| Adapter Buffer (ADB) | 3.5 μl |
| Total | 5 μl |
Prepare the remaining reagents in accordance with the reagent preparation page on the on-screen display.
Once completed click Next to proceed.
Once your flow cell check has successfully completed, set up your sequencing run conditions on the on-screen display:
- Select the sequencing time limit, or to stop run when the flow cell pores are depleted.
- Select a data target.
- Select whether to perform:
3.1. A flow cell flush to return the used flow cell.
3.2. A flow cell wash using the Flow cell wash kit (EXP-WSH004) to reuse your flow cell.
Note: Reagent volumes and guidance for flow cell wash or flush will be given on the deck loading page. If you would like to perform a flow cell wash for re-use it is recommended to thaw the wash reagents at the same time as the library preparation reagents.
For more information on the run conditions please refer to the ElysION User Guide.
Reagent and consumables requirements
Please consider the following when preparing and loading your reagents and consumables into the ElysION device to mitigate risk of workflow failure and equipment damage:
- Ensure that the correct consumables are used with each reagent.
- Spin down all samples and reagents, making sure they do not contain bubbles.
- Ensure plates are flat in their deck position and sit within the barriers on the deck, and tubes are fully inserted into the rack.
Set up the ElysION deck according to the deck layout outlined in the UI of the on-screen display.
Note: The position of the tip boxes and reagents will change depending on the sample count, and run setup. Please ensure you are following the instructions on the on-screen display correctly for your run.
Insert two empty waste bins into the disposable waste drawer below the deck.
Close the door of the ElysION device.
Click "Begin run" to start the automated library preparation and sequencing.
Data analysis will automatically be carried out by the ElysION device once your sequencing run is complete.
The analysis pipeline used is the wf-bacterial-genomes.
For more information on how to access your sequencing data and the analysis outputs please consult the ElysION User Guide.
Once the run is finished, unload labware, empty the bins, and discard or store in the freezer any unused reagents.
8. Issues during DNA extraction and automated library preparation
Below is a list of the most commonly encountered issues, with some suggested causes and solutions.
We also have an FAQ section available on the Nanopore Community Support section.
If you have tried our suggested solutions and the issue still persists, please contact Technical Support via email (support@nanoporetech.com) or via LiveChat in the Nanopore Community.
Low sample quality
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Inefficient lysis | Enzyme activity has degraded in the solution or the isolate species is hard to lyse. | - Make a fresh enzyme solution. - Follow the hard to lyse gDNA extraction option. - Increase the enzyme incubation for longer than 10 minutes. |
| Low DNA concentration | Low input into the extraction method | - Check the cell input used - Add more input and perform the extraction again |
| Low DNA integrity number (DIN) | Low quality or concentration of sample input | - Repeat the extraction with freshly made enzyme solution |
| Low sequencing yield | Low sample concentration | - Check the DNA concentration and quality. RNA presence may affect quantification of total DNA. |
| Low DNA purity (Nanodrop reading for DNA OD 260/280 is <1.8 and OD 260/230 is <2.0–2.2) | The DNA extraction method does not provide the required purity | The effects of contaminants are shown in the Contaminants Know-how piece. Please try an alternative extraction method that does not result in contaminant carryover. Consider performing an additional SPRI clean-up step. |
ElysION device troubleshooting
For commonly encountered issues please refer to the ElysION User Guide.
For in-depth troubleshooting please refer to the Set-up and operating manual: Early access ElysION provided with your ElysION device.
For additional customer support contact the nanoporetech support channels.
9. NO-MISS Pause for QC
Introduction
The Nanopore Only Microbial Isolate Sequencing Solution (NO-MISS) assay has been configured to contain an optional pause once the extraction has completed, but before the eluate is transferred into the rapid barcoding reaction. This pause allows the user to perform sample QC and/or normalise their samples to 200 ng. Normalisation has been shown to improve the output of the ElysION NO-MISS assay with only an additional 30 minutes of hands-on time.
Protocol
The NO-MISS assay by default does not include a scheduled pause to allow QC. This feature is activated by the user through the Method configurator in the ElysION UI, which will create an assay variant with the pausing feature enabled by default. When running this variant assay, the lab user interacts with the samples following completion of the extraction ~ 1 hour into the assay run.
Configuring the method
Select 'System' in the bottom left corner of the ElysION software, on the touch screen monitor, then 'Method configurator'.

Select the ‘Create new variant’ option of the NO-MISS method for editing.
Note: There may be multiple NO-MISS assays available to configure.
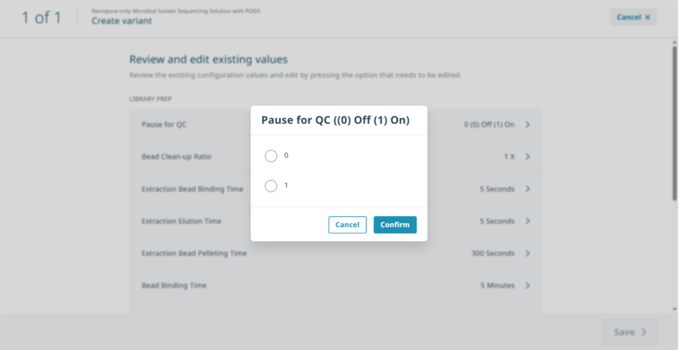
In ‘Review and edit existing values’ select ‘Pause for QC’ then select ‘1’ to activate the pause and ‘Confirm’.

Edit other variables as desired, then select ‘Save’.

The new method will appear in ‘Run method’ with the same name as its original assay and ‘.vX’ at the end, where X is the number of the new assay made.

Manual interactions
In the ElysION application, press the 'Run method' tab on the left side of the window.
To begin the method, select it from the list of available methods. Then press 'Next' at the bottom right corner of the screen.
Set up the NO-MISS run following the UI instructions and start the assay.
The run overview page of the ElysION UI will show the next step as 'Pause for QC'. This will occur around 1-1.5 hours into the protocol depending on sample count. Once the extraction is complete, the robot will pause, and the door will unlock.
The extraction eluates are in a PCR plate on deck position B3. There will be 30 µl of sample to QC from. All samples are in the same well ID locations as stated in the sample sheet given by the user.